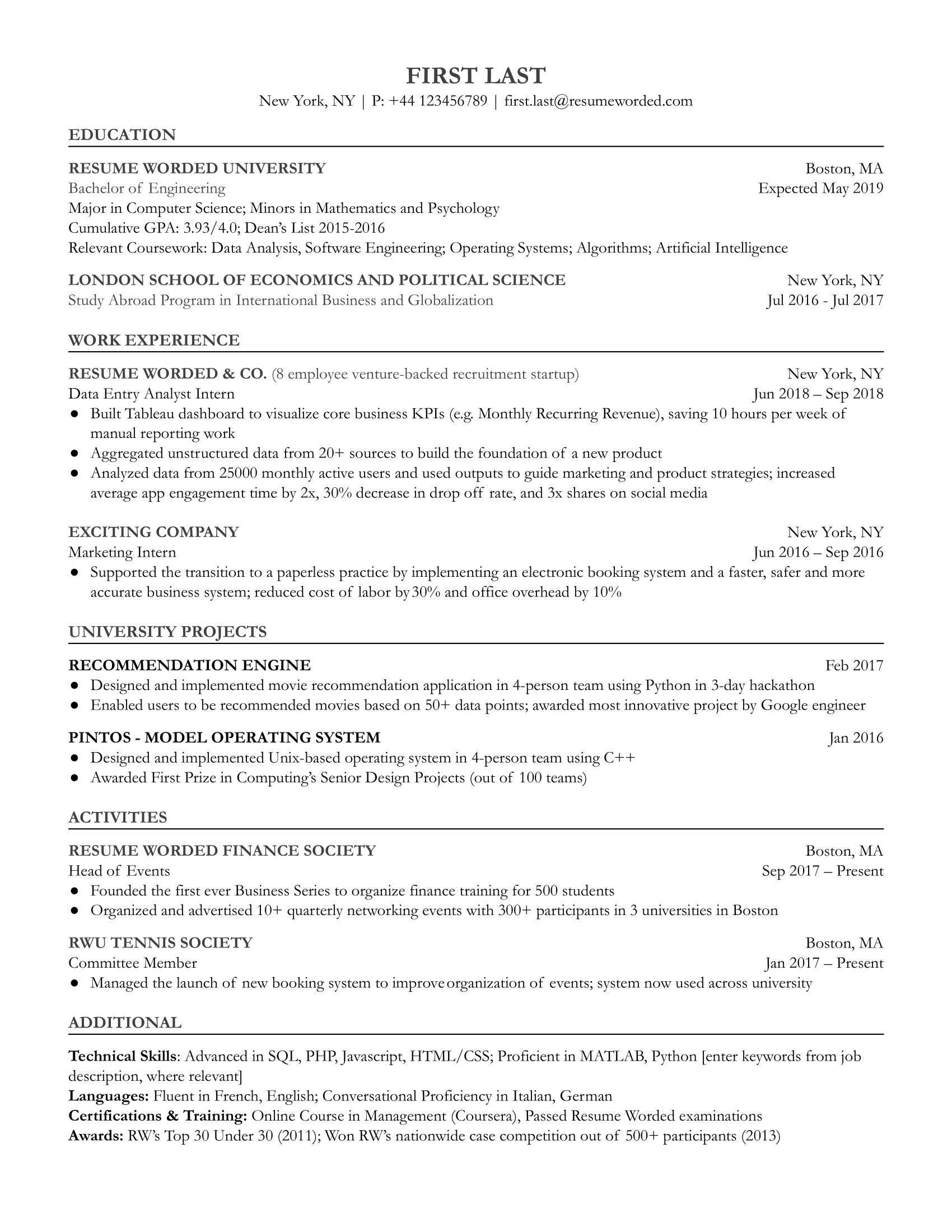
Data entry involves inputting information into systems, while data analysts interpret and extract insights from data. Both roles are crucial for data management.
Data entry clerks focus on accurately and efficiently entering data into databases, spreadsheets, or software programs. They ensure data integrity and consistency. Data analysts, on the other hand, analyze and interpret data to provide meaningful insights and drive strategic decisions.
They use statistical tools and software to identify trends, correlations, and patterns within the data. While data entry is more about accuracy and speed, data analysis requires critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and a deep understanding of data science. Both roles are essential in the data-driven world, but they serve different purposes and require distinct skill sets.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Data Entry And Data Analysis: Unveiling The Basics
Understanding the difference between Data Entry and Data Analysis is crucial. Both play essential roles in managing information. But they serve different purposes. This section will break down their basics.
Clarifying Data Entry
Data Entry involves inputting data into systems. This can be done manually or electronically. The primary task is to ensure data accuracy and completeness.
- Entering customer information
- Updating databases
- Transcribing documents
People in data entry positions are detail-oriented. They must ensure the data is error-free. They often use software like Excel or specialized databases.
Decoding Data Analysis
Data Analysis goes beyond entering data. It focuses on interpreting and extracting insights from data. Analysts use various tools to make sense of the data.
- Identifying trends
- Creating reports
- Making data-driven decisions
Data Analysts use tools like Python, R, and SQL. They need strong analytical skills. They help organizations make informed decisions based on data.
| Aspect | Data Entry | Data Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Task | Input data | Analyze data |
| Skills Required | Attention to detail | Analytical skills |
| Tools Used | Excel, Databases | Python, R, SQL |
Roles And Responsibilities
Data Entry Operators and Data Analysts have unique roles. Their responsibilities differ significantly. Knowing these differences can help you understand each job better.
Task Breakdown: Data Entry Operator
Data Entry Operators handle various tasks. Their primary role is entering data into systems.
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Input | Enter information into databases accurately. |
| Data Verification | Check and correct data entries for accuracy. |
| Documentation | Maintain records of entered data. |
They use various tools. These tools help in efficient data management.
Task Breakdown: Data Analyst
Data Analysts focus on data interpretation. They transform raw data into actionable insights.
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Collection | Gather data from various sources. |
| Data Cleaning | Remove inaccuracies and inconsistencies. |
| Data Analysis | Analyze data to find trends and patterns. |
| Reporting | Create reports based on analysis. |
They use advanced software. This software helps in data analysis and visualization.
Skill Sets: A Comparative Look
Understanding the skill sets for data entry and data analysis is crucial. Each role demands unique abilities and expertise. Let’s explore the essential skills required for each role.
Essential Skills For Data Entry
Data entry specialists need to be precise and quick. Here are some key skills:
- Typing Speed: Fast and accurate typing is essential.
- Attention to Detail: Ensures data accuracy.
- Basic Software Knowledge: Proficiency in MS Excel and Word.
- Time Management: Meets deadlines efficiently.
- Data Privacy: Protects sensitive information.
Analytical Skills For Data Analysis
Data analysts must have strong analytical and technical skills. These include:
- Statistical Analysis: Understands and applies statistical methods.
- Programming Skills: Proficiency in SQL, R, or Python.
- Data Visualization: Creates charts and graphs to present data.
- Critical Thinking: Identifies patterns and insights.
- Problem-Solving: Develops solutions based on data findings.
Credit: resumeworded.com
Tools Of The Trade
Understanding the tools used in data entry and data analysis is crucial. Each role requires a different set of tools to perform effectively. Below, we explore the specific software and advanced tools used by data entry professionals and data analysts.
Software For Data Entry
Data entry professionals rely on basic software tools. These tools help them input, manage, and organize data efficiently.
- Microsoft Excel: Widely used for its simplicity and versatility. Excel helps in organizing data into rows and columns.
- Google Sheets: A cloud-based alternative to Excel. It allows for real-time collaboration and sharing.
- Database Software: Software like Microsoft Access helps manage large datasets effectively.
- Word Processing Tools: Tools like Microsoft Word assist in entering textual data.
Advanced Tools For Data Analysis
Data analysts use advanced tools to analyze and interpret data. These tools help in drawing meaningful insights from complex datasets.
- SQL: SQL is used for querying and managing databases. It is essential for handling large datasets.
- R: R is a programming language designed for statistical analysis. It helps in data visualization and modeling.
- Python: Python is popular for its libraries like Pandas and NumPy. These libraries are powerful for data manipulation and analysis.
- Tableau: Tableau is a data visualization tool. It helps create interactive and shareable dashboards.
- Power BI: Power BI is another visualization tool by Microsoft. It integrates well with other Microsoft products.
| Data Entry | Data Analysis |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Excel | SQL |
| Google Sheets | R |
| Database Software | Python |
| Word Processing Tools | Tableau |
| Power BI |
Impact On Decision-making
In today’s data-driven world, understanding the difference between data entry and data analysis is crucial. Both roles significantly impact decision-making processes. Let’s explore how each contributes to informed choices.
Data Entry’s Role In Information Handling
Data entry specialists focus on accurate data input. They ensure all information is up-to-date and error-free. This role involves:
- Entering data into systems
- Maintaining data integrity
- Updating records regularly
Proper data entry creates a solid foundation. It allows organizations to trust their data. Accurate data entry is vital for effective decision-making. It minimizes errors and ensures reliable information.
Data Analysts: Steering Strategic Decisions
Data analysts play a critical role in interpreting data. They analyze data sets to find patterns and trends. This analysis helps in:
- Identifying business opportunities
- Predicting future trends
- Making strategic decisions
Analysts use various tools and techniques. They transform raw data into actionable insights. These insights guide companies in making informed decisions. Data analysts help steer the business in the right direction.
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
| Aspect | Data Entry | Data Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Accurate data input | Data interpretation |
| Key Tasks | Entering and updating data | Analyzing and interpreting data |
| Impact on Decisions | Provides reliable data | Guides strategic choices |
Both roles are essential. Together, they ensure organizations make well-informed decisions. Proper data entry lays the groundwork, while data analysis provides the insights.
Career Trajectories And Growth
The career paths for data entry professionals and data analysts vary significantly. Each role offers unique growth opportunities. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right path.
Pathways For Data Entry Professionals
Data entry professionals often start with basic data entry tasks. These tasks include inputting data into databases or spreadsheets.
As they gain experience, they may advance to data verification roles. These roles involve checking data for accuracy and completeness. Some may move into administrative support positions.
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Basic Data Entry | Inputting data into systems |
| Data Verification | Checking data for errors |
| Administrative Support | Supporting office tasks |
Career Advancement For Data Analysts
Data analysts start with interpreting data and creating reports. They use tools like Excel, SQL, and statistical software.
With experience, they can become senior data analysts. These roles involve more complex data analysis and strategic decision-making.
- Entry-Level Data Analyst: Analyzing and reporting data
- Senior Data Analyst: Advanced data analysis and strategy
- Data Scientist: Developing algorithms and predictive models
Some may advance to data scientist roles. Data scientists develop advanced algorithms and predictive models. This role often requires expertise in machine learning.

Credit: www.ziprecruiter.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Can You Move Up From Data Entry?
Yes, you can advance from data entry roles. Gain skills in data analysis, software proficiency, or project management for better opportunities.
What Is The Higher Position Than A Data Analyst?
A higher position than a data analyst is a data scientist. Data scientists analyze complex data and create predictive models.
What Does An Entry Data Analyst Do?
An entry data analyst collects, processes, and analyzes data. They create reports, identify trends, and support decision-making. They use tools like Excel and SQL to manage data efficiently. Their goal is to help businesses make informed decisions by providing accurate data insights.
Is Data Entry The Same As Coding?
No, data entry is not the same as coding. Data entry involves inputting information into systems, while coding requires writing software programs.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between data entry and data analysis is crucial. Data entry focuses on inputting information accurately. Data analysts interpret that data to provide insights. Both roles are essential for a business’s data management. Knowing their distinctions can help guide career choices and organizational needs.

