Freelancers work on specific projects for various clients. Self-employed individuals run their own business and control all aspects.
Freelancing and self-employment share similarities but differ in nature. Freelancers often juggle multiple clients, providing specialized services on a project basis. They enjoy flexibility but lack long-term stability. Self-employed individuals run their own business, handling everything from marketing to finances.
They have more control but also face greater responsibilities and risks. Both offer independence and the potential for growth, but each has unique challenges and benefits. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right path for your career goals. Whether freelancing or self-employment suits you, both can provide rewarding opportunities and the freedom to work on your own terms.
Freelance Vs. Self-employed: Clarifying The Concepts
Understanding the difference between being a freelancer and self-employed is crucial. These terms are often used interchangeably. Yet, they hold distinct meanings and implications.
Common Misconceptions About Freelancing And Self-employment
Many people think freelancing and self-employment are the same. This is a common misconception. Both involve working independently. But, there are key differences.
- Misconception 1: Freelancers and self-employed individuals have the same tax rules.
- Misconception 2: Freelancers always work on short-term projects.
- Misconception 3: Self-employed people always own a business.
Key Definitions: Freelancer And Self-employed Individual
Let’s break down the definitions:
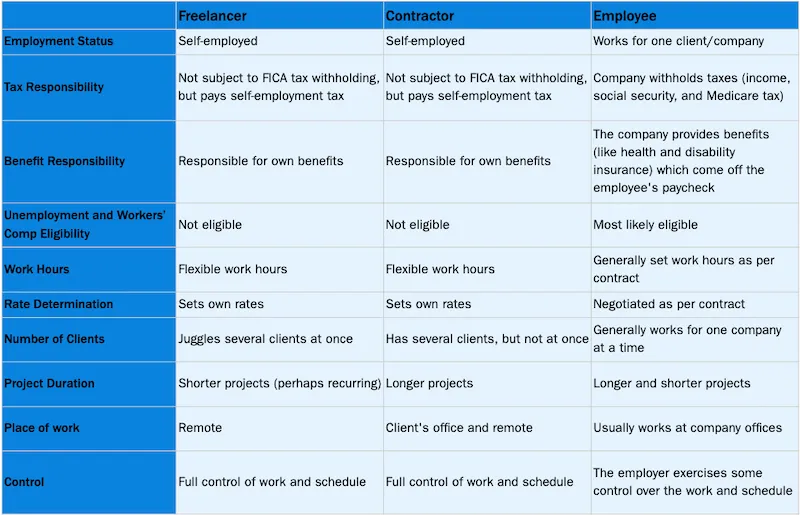
| Freelancer | Self-Employed Individual |
|---|---|
| A freelancer works for multiple clients. They often take on short-term projects. | A self-employed person runs their own business. They might have employees or work solo. |
| Freelancers usually work on a project basis. They do not have long-term commitments. | Self-employed people may have long-term contracts. They could offer ongoing services. |
| Freelancers are often seen in creative fields. Think writers, designers, and developers. | Self-employed individuals can be in any industry. They might be consultants, shop owners, or tradespeople. |
Understanding these differences helps clarify the roles. It also aids in making informed career choices.
Credit: www.freshbooks.com
Legal And Tax Implications
Understanding the legal and tax implications of being freelance versus self-employed is crucial. It helps you avoid legal pitfalls and manage your finances effectively. Both statuses have unique requirements and responsibilities. Let’s explore these differences in detail.
Tax Responsibilities For Freelancers Versus Self-employed
Freelancers and self-employed individuals both need to pay taxes. But the responsibilities differ.
Freelancers usually work on a project-by-project basis. They often have multiple clients and inconsistent income. They must file estimated taxes quarterly. These payments cover income tax and self-employment tax.
Self-employed individuals typically run their own businesses. They might have employees and steady revenue. They also pay estimated taxes quarterly. But their tax filings can be more complex. They may need to file additional forms for business expenses and employee wages.
| Category | Freelancers | Self-Employed |
|---|---|---|
| Income Source | Multiple clients | Own business |
| Tax Payments | Quarterly estimates | Quarterly estimates |
| Complexity | Lower | Higher |
Business Registration And Legal Entity Differences
Freelancers and self-employed individuals must register their businesses. But the process varies.
Freelancers often operate as sole proprietors. This setup requires minimal paperwork. They may need a business license or permit, depending on their location. They usually do not register as a separate legal entity.
Self-employed individuals might choose different business structures. Options include sole proprietorship, LLC, or corporation. Each structure has unique legal and tax implications. For example, an LLC offers limited liability protection. But it involves more paperwork and fees.
- Sole Proprietorship: Simple setup, minimal paperwork, no separate legal entity.
- LLC (Limited Liability Company): Offers liability protection, more paperwork, separate legal entity.
- Corporation: High complexity, high costs, separate legal entity, potential tax benefits.
Control And Flexibility In Work
Freelancers and self-employed individuals both enjoy a high level of control and flexibility. This freedom allows them to shape their work environment and schedules. Yet, there are distinct differences in how each manages their work life.
Autonomy In Choosing Projects
Freelancers often have the liberty to choose specific projects. They can decide which clients to work with and set their own terms. This autonomy lets them align their work with their interests and skills.
Self-employed individuals may have more consistent work. They often own a business or service, so they can’t always pick and choose. Their focus is on maintaining their business and client satisfaction.
Work-life Balance And Scheduling
Freelancers have the ability to create their own schedules. They can work from any location and at any time that suits them. This flexibility can lead to a better work-life balance.
Self-employed people also set their own schedules. Yet, they might find themselves working longer hours. The responsibility of running a business can demand more time and effort.

Credit: www.freshbooks.com
Income And Financial Stability
Understanding income and financial stability is key for freelancers and self-employed individuals. This section explores how each option impacts earnings and financial security.
Predictability Of Earnings
Freelancers often face variable income. Their earnings depend on project availability and client payments. Sometimes, they have many projects at once. Other times, they may have none.
Self-employed individuals, like small business owners, usually have more predictable income. They can forecast earnings based on sales, services, or client contracts.
| Freelance | Self-Employed |
|---|---|
| Variable income | More predictable income |
| Dependent on projects | Dependent on business performance |
| Income can fluctuate | Steady income possible |
Diversification Of Income Sources
Freelancers often diversify income by working with multiple clients. They can take on various projects in different fields. This helps spread financial risk.
Self-employed individuals usually focus on one business. They may diversify within their business. For example, a bakery might offer catering services or sell products online.
- Freelancers: Multiple clients, various projects, spread financial risk.
- Self-Employed: One business focus, possible diversification within business.
Building A Brand And Reputation
Freelancers and self-employed individuals both need to build a strong brand and reputation. Their approach to achieving this can vary significantly. Let’s delve into the distinct strategies each group uses.
Personal Branding For Freelancers
Freelancers often focus on creating a personal brand. This involves showcasing their unique skills and personality. They use platforms like LinkedIn, personal websites, and social media to highlight their expertise.
- Portfolio: A well-crafted portfolio highlights past work and client feedback.
- Social Media: Consistent posts on platforms like Twitter and Instagram.
- Networking: Join industry groups and attend events.
Freelancers aim to become recognizable figures in their niche. They rely heavily on their online presence and word-of-mouth referrals.
Business Reputation For Self-employed Individuals
Self-employed individuals often manage a business or a company. Their reputation hinges on the brand they build around their business. This often involves a more formal and structured approach.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Brand Identity | Includes logo, mission, and values. |
| Customer Service | Providing excellent support and services. |
| Quality Assurance | Ensuring high-quality products or services consistently. |
They often invest in marketing strategies and customer service to build trust and credibility. Their goal is to establish a solid business reputation that attracts and retains clients.

Credit: ddiy.co
Long-term Growth And Scalability
Both freelancing and being self-employed offer unique growth opportunities. Understanding how to scale each model is crucial for long-term success. Let’s dive into the specifics.
Scaling Freelance Operations
Scaling as a freelancer involves increasing your client base without overextending yourself. Here are some key strategies:
- Automate Repetitive Tasks: Use tools to automate invoicing and communication.
- Outsource: Hire virtual assistants for administrative tasks.
- Specialize: Focus on a niche to become an expert and charge premium rates.
- Network: Build connections to get referrals and repeat business.
Expanding A Self-employed Business
Expanding a self-employed business requires a different approach. Here’s how you can achieve growth:
- Hire Employees: Bring in skilled workers to handle more projects.
- Invest in Marketing: Use online and offline methods to attract clients.
- Diversify Services: Offer additional services to meet varied client needs.
- Upgrade Tools: Use advanced software to improve efficiency.
| Aspect | Freelance | Self-Employed |
|---|---|---|
| Team Size | Mostly solo, occasional outsourcing | May include employees |
| Work Scope | Project-based | Service or product-based |
| Scalability | Limited by individual capacity | Higher potential with a team |
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Freelance The Same As Self-employed?
Freelance and self-employed are similar but not identical. Freelancers work on projects for various clients. Self-employed individuals run their own businesses and may have employees. Both manage their own taxes.
Is It Better To Say Freelance Or Self-employed On Resume?
Both terms work, but “self-employed” sounds more professional. “Freelance” can highlight project-based work. Choose based on context.
Is A 1099 Self-employed Or Freelance?
Yes, a 1099 form is for self-employed or freelance workers. They report income independently, not as employees.
Is A Freelancer A Self-employed Person Who?
Yes, a freelancer is a self-employed person who offers services to clients on a project or contract basis.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between freelance and self-employed is crucial. Freelancers often work on multiple short-term projects. Self-employed individuals typically run their own business. Knowing these distinctions helps you navigate your career path effectively. Make informed decisions to achieve your professional goals.


